
Also that research expenditure is only classified as development expenditure if it meets the criteria specified in IAS® 38 Intangible Assets. Completeness – that there are no omissions and assets and liabilities that should audit management assertions be recorded and disclosed have been. In other words there has been no understatement of assets or liabilities.
Accuracy
There are numerous audit assertion categories that auditors use to support and verify the information found in a company’s financial statements. When performing an audit, it is the auditor’s job to obtain the necessary evidence to verify the assertions made in the financial statements. Whether you’re using accounting software or recording transactions in multiple ledgers, the audit assertion process remains the same.
- There is a reference to transactions being appropriately aggregated or disaggregated.
- In other words, management did not record any revenue transactions that occurred after year-end.
- In this article, we will discuss the nature and the usage of each assertion as well as how important it is for management and auditors.
- For example, when reporting revenue on the income statement, management is implying that genuine sales occurred (none are fabricated).
- The general audit objectives described in Exhibit 7-2 may be applied to any category of transaction and the related account balances.
Presentation and Disclosure Assertions in Auditing
The following lists the types of audit assertions in the three areas of a financial audit. Each also provides the assertion meaning or definition to help one understand how each is used in an assessment. Assertions help auditors identify and address risks of material misstatement, enabling them to focus their audit procedures on areas with https://www.bookstime.com/ a higher likelihood of error or fraud. Transactions and events disclosed in the financial statements have occurred and relate to the entity. Describe substantive procedures the auditor should perform to obtain sufficient and appropriate audit evidence in relation to the VALUATION of X Co’s inventory. Accuracy, valuation and allocation – means that amounts at which assets, liabilities and equity interests are valued, recorded and disclosed are all appropriate.

Audit Assertions: Everything You Need to Know

Assertions assist auditors in considering a wide range of issues that are relevant to the authenticity of financial statements. The consideration of management assertions during the various stages of audit helps to reduce the audit risk. The implicit or explicit claims by the management on the preparation and appropriateness of financial statements and disclosures are known as management assertions.

What Are the Audit Processes? 7 Key Processes You Should Know
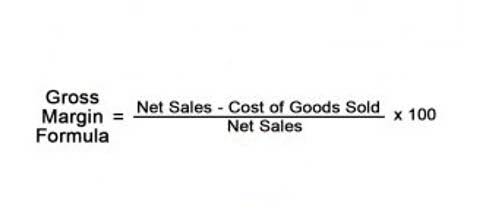
Without these assertions in place, it is considerably harder for stakeholders to comprehend the financial statements. Completeness is a crucial audit assertion since it relates to the balance sheet and income statement. For example, they must ensure companies have recognized all items in fixed assets that they must have.

Sufficient and appropriate disclosures have been made on related transactions, events and account balances. When financial statements are being prepared, there are certain elements that need to be borne in mind by the accountants. The preparation itself requires certain claims that need to make pertaining to the preparation of financial statements. While one does not prevail over another, auditors can still focus on some more.
- Unless you’re an auditor or CPA, you’ll never have to worry about testing audit assertions, and if you continue to enter financial transactions accurately, you won’t have much to worry about during the audit process.
- The Ascent, a Motley Fool service, does not cover all offers on the market.
- For example, when presenting the inventory account on the balance sheet, management is asserting that all the inventory items exist.
- This is particularly important for those accruing payroll or reporting inventory levels.
- All disclosures that should have been included in the financial statements have been included.
- Completeness – this means that transactions that should have been recorded and disclosed have not been omitted.
- For example, audits are conducted on a sample basis, and the possibility of material misstatements not being detected cannot be entirely eliminated.
- Management of these corporations was now required to assess and assert as to the effectiveness of the organization’s internal controls over financial reporting.
- Audit assertions form to be the basis of the entire audit planning and procedural phase.
Confirms the proceeds of sale so is more relevant to accuracy or valuation.D. During the interim audit, the system of internal control is documented and evaluated. This will determine the mix of tests of control and substantive procedures but both will tend to focus on transactions that have occurred so far in the period. It is the auditor’s responsibility to determine that these items are properly disclosed in the financial statements. https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc For instance, the reporting of a company’s accounts receivable account does not provide a guarantee that the customer will pay the accounts receivable amount owed.

Leave a Reply